Formulation efficiency
and quick problem solving
Formulation efficiency
and quick problem solving
Formulation efficiency and quick problem solving
Typical challenges for cosmetic formulators
- Stability of emulsions
- Skin feel modification
- Viscosity control
- pH drift
- Color change
- Scaling-up
Systematic development is key
- Big changes are better … – to see and feel a real difference
- Min/Max batches and then mix them
- Cold processible co-emulsifier for time-saving tests
- Modifying the batch at room temperature to act quickly (oils / emulsifier / homogenizing)
- Centrifuge as top/flop measurement system
- Heat stability data (40°/50°) ➔ color change / creamy vs. glassy / droplet size increase
- Microscope visualization and droplet size comparison


Sensorial formulation adaptation process
As an example, your marketing wants to have the product somewhat lighter or smoother … How can we adjust and work systematically in the lab?
Key factors are:
- Choice of emulsifier
- Choice of oil components
- Choice of additives
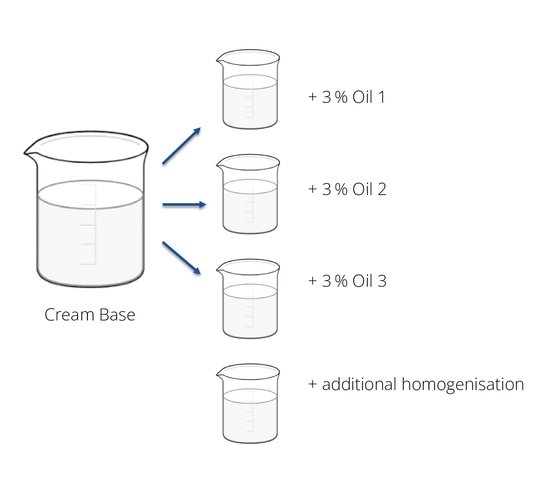
1. Choosing an appropriate cream base / project cream base
2. Dividing into several portions
3. Adding oils at RT, homogenise softly, then evaluate their influence on sensorial aspects by adding enough material to clearly feel a difference
4. If the level of oil was too high, mix again with cream base to “dilute” the effect until you like it
What does this look like?
Understanding the system of emulsions
To initiate the right actions, it is essential to understand the system of emulsions.
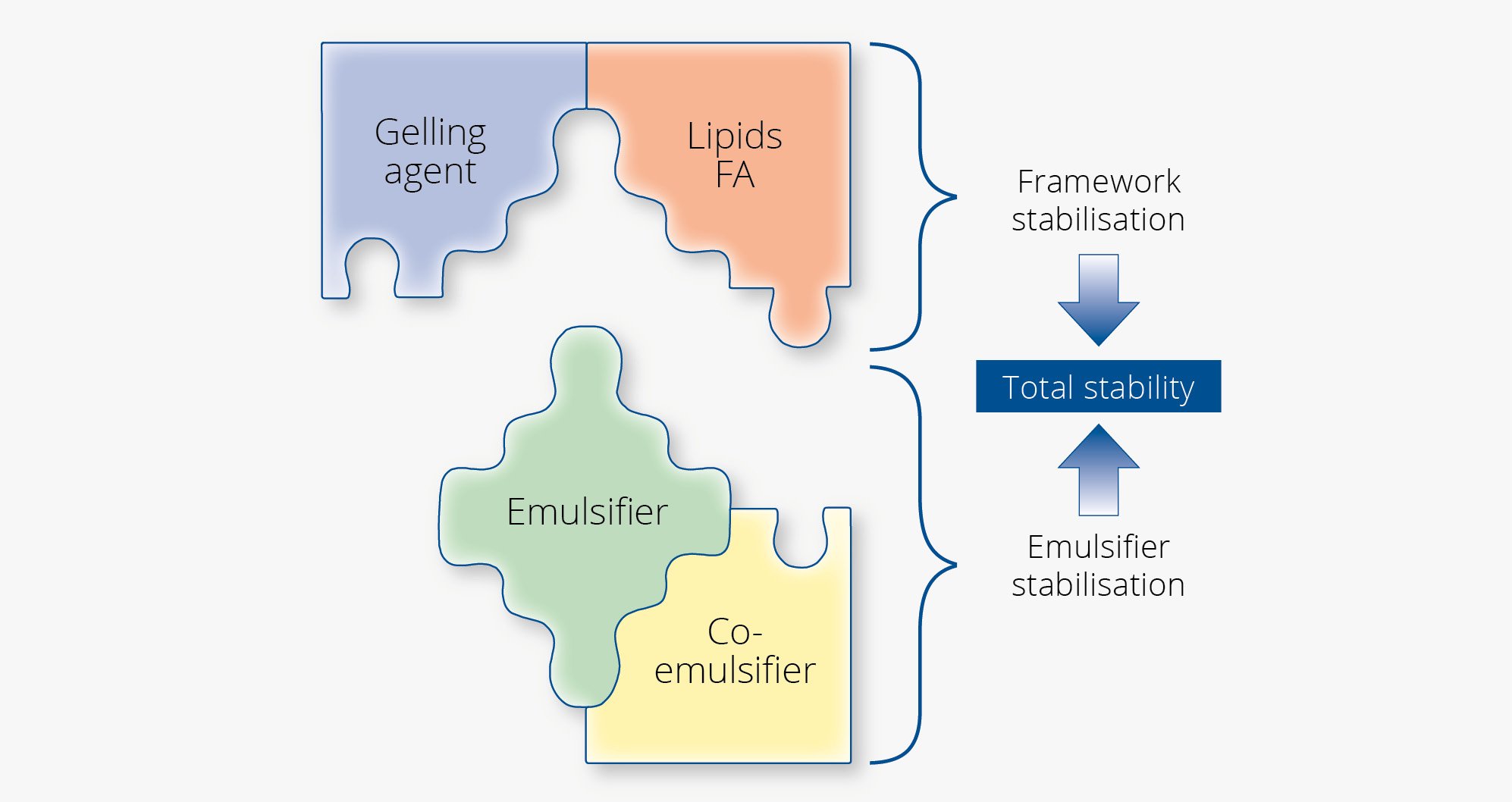
The components of an emulsion
The interaction of gelling agent, emulsifier, fatty alcohol and co-emulsifier defines the consistency and the stability of the emulsion.
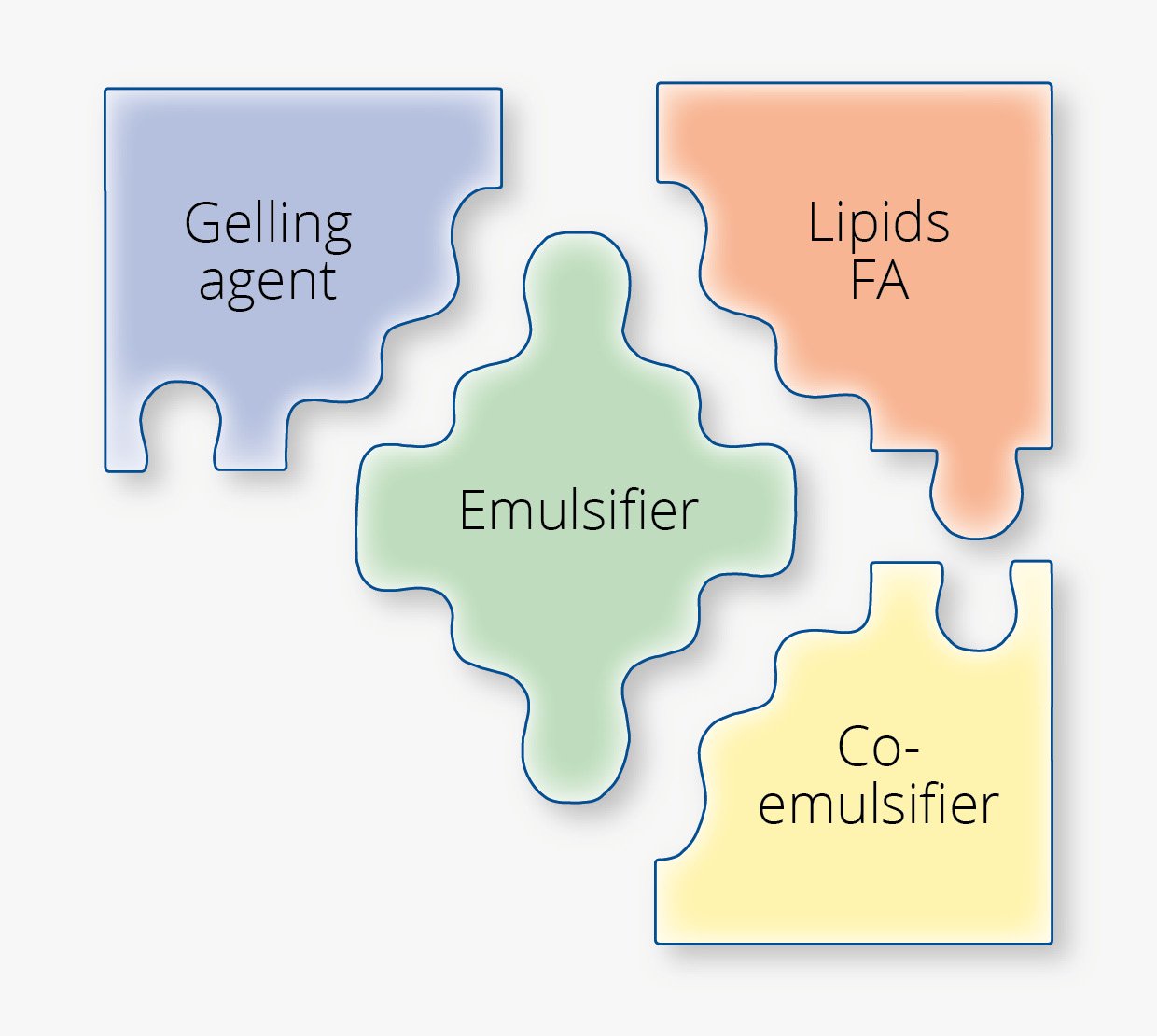
Potential components of an emulsion
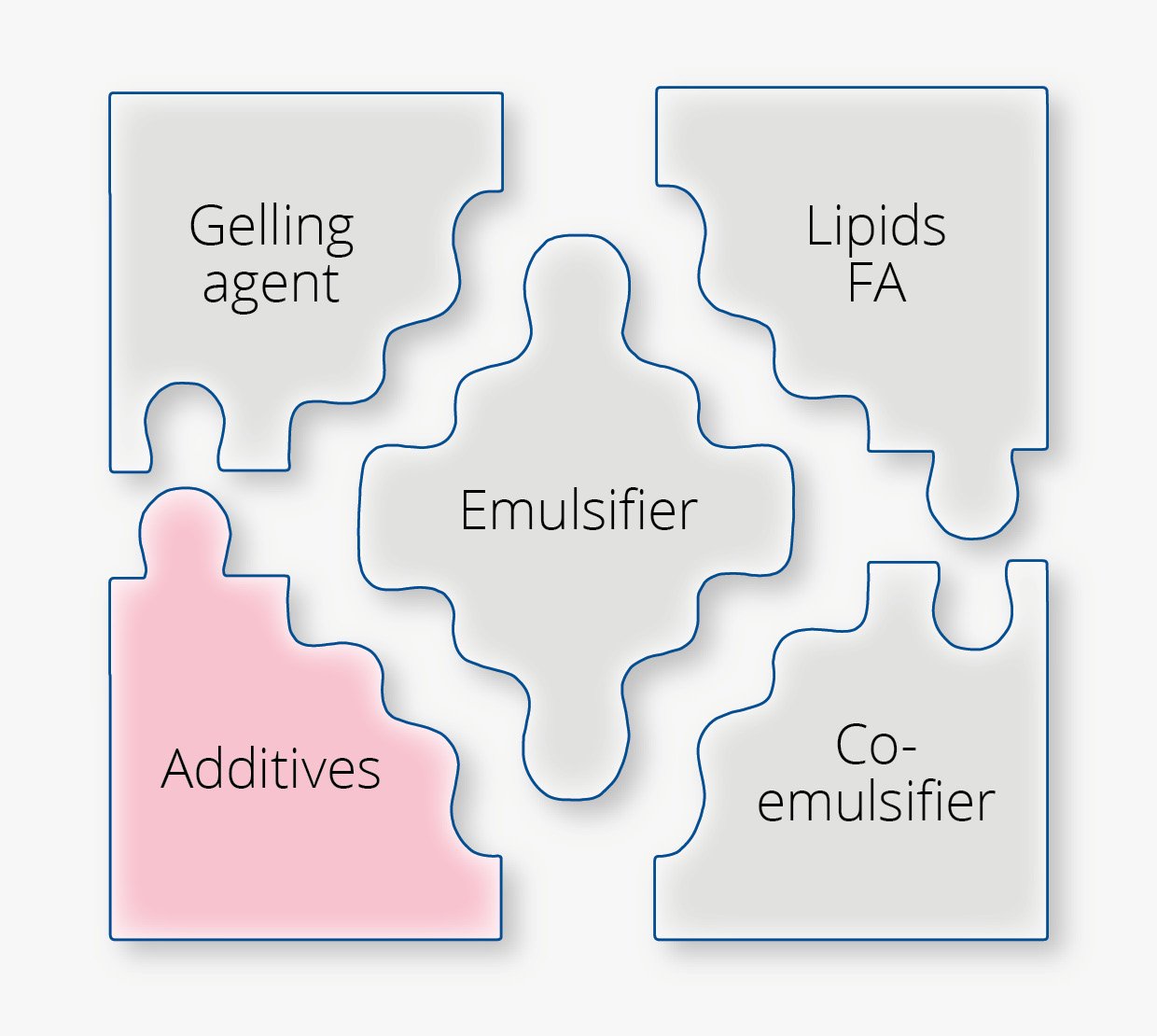
Additives such as fragrance, active ingredients or preservatives can disrupt the structure, consistency and stability of the emulsion by weakening the stabilizing components.
Your personal contact

Sandra Gut
Senior Application Laboratory Manager Cosmetics
RAHN (UK) Ltd.
