3D Printing
in Dentistry
3D Printing
in Dentistry
3D Printing in Dentistry – A New Landmark in Affordable Healthcare
The integration of Photopolymer 3D printing in dentistry has revolutionized the field by offering enhanced precision, improved materials, streamlined processes and lower costs. Photopolymers play an invaluable role for an affordable, improved and cost-efficient healthcare system.
Find out how 3D printing in dentistry offers multiple usage applications, such as implants or orthodontic treatment and how it customises the treatment of every single patient due to the bespoke properties of photopolymer resin.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a manufacturing process that creates 3D objects by building them layer by layer from a digital 3D model. Vat Photopolymerization is a specific type of 3D printing technology that utilises photopolymers as the material for creating these objects. Another advanced 3D printing technique, material jetting, also offers significant benefits in producing highly detailed and precise objects, making it a valuable tool in various industries, including healthcare and dentistry.
Photopolymers undergo a chemical reaction when exposed to specific wavelengths of light. This reaction causes the liquid photopolymer to solidify and harden, allowing it to be built up layer by layer to form the final 3D object.
Photopolymer 3D printing is often used for applications that require high levels of detail, accuracy, and smooth surface finishes.
It can be used in various industries and scenarios, such as 3D printing in the automotive industry, 3D printing in construction, and 3D printed jewellery.

Photopolymer 3D printing in healthcare advances at a similar pace. 3D printing in the dentistry field can decentralise, customise, streamline and speed up the manufacturing process.
Applications of 3D printing in dentistry
Photopolymer 3D printing in dentistry has already gone a long way and has led to an improved patient care, reduced chair time, enhanced treatment outcomes and better cost-efficiency for dental practices and academic purposes alike.
3D printing for dental implants
By using 3D printing for dental implants, professionals can create patient-specific implants tailored to the individual's unique anatomy and needs. 3D printing for dental implants has opened up new possibilities for personalised and advanced implant solutions, leading to improved outcomes and satisfaction for both patients and dental professionals.
Orthodontic treatment
3D printing in dentistry allows for the production of custom orthodontic brackets tailored to each patient's tooth anatomy. These brackets can be designed to fit securely and efficiently. As an example, photopolymer 3D printing is widely used to create clear aligners. Orthodontists start by taking digital scans of the patient's teeth, which are then used to design a series of aligners that gradually move the teeth into the desired positions. In this process, the moulds are 3D printed, while the aligners are thermoformed by using plastic films such as polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU).
Enhancing Precision in Dental Implants with 3D Printing
3D printing is utilised to manufacture various prosthetic components used in the implant restoration process, such as abutments and crowns. These components can be precisely designed to fit the implant and the patient's surrounding teeth, resulting in improved aesthetics and functionality. This level of customization ensures a better fit and reduces the need for extensive modifications during the surgery.
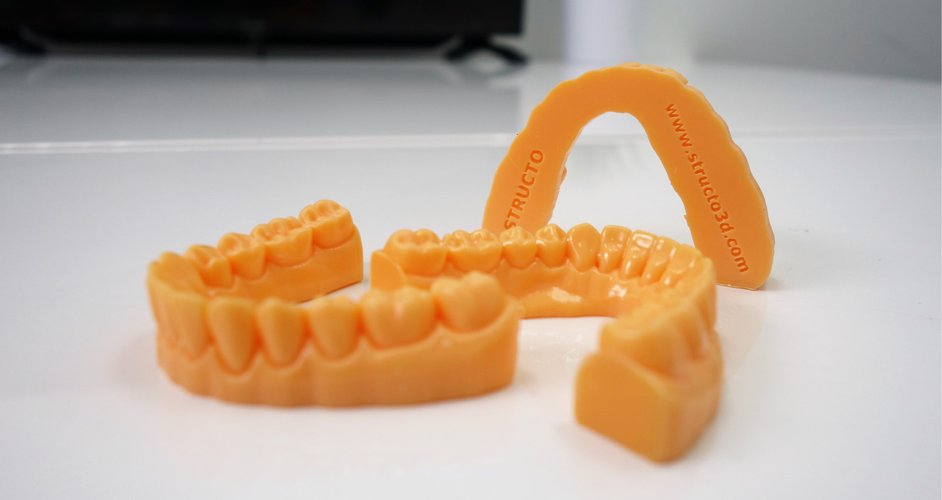
Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics is a branch of dentistry focused on the restoration and replacement of damaged or missing teeth and other oral structures. 3D printing for dental implants is tailored to each patient's unique oral anatomy, ensuring optimal fit and functionality. 3D printing also enables the production of temporary restorations for immediate use, reducing turnaround time and enhancing patient convenience.
Imaging and reconstruction
Dentists can utilise this technology to create precise models of patients' teeth and jaws based on scans from X-rays or CT scans. These models enable detailed analysis for treatment planning, such as orthodontic adjustments or implant placements. Additionally, 3D printing facilitates the fabrication of custom-made dental implants, crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Surgical guides
Photopolymer 3D printing has become a game-changer in the production of surgical guides for various dental procedures, including orthodontics, implantology and maxillofacial surgery. Photopolymer 3D printing is ideal for surgical guides because it can achieve high levels of detail and accuracy, which is crucial for successful surgical outcomes.
Surgical guides are essential tools that aid surgeons in performing precise and minimally invasive procedures. During the surgery, the surgical guide is placed over the patient's anatomy and guides the surgeon to make precise incisions, position implants or to perform other procedures. The guide ensures that the surgical actions are carried out exactly as planned, reducing the risk of errors or complications.
Educational purposes
3D printing has opened up new possibilities for dental education and training, allowing dental students and professionals to gain practical experience and improve patient communication. Photopolymer 3D printing allows the creation of highly accurate and detailed anatomical models of teeth, jaws, and oral structures. These physical models provide dental students with hands-on learning opportunities.
3D-printed models can be used for surgical simulations, allowing dental students to practise various dental procedures in a risk-free environment. This includes practising tooth extractions, implant placements and other surgical techniques. Dental schools can even use 3D printing to produce patient-specific models based on real clinical cases. These models serve as teaching tools, allowing students to better explore different treatment options and develop treatment plans for specific patients.
Advantages of 3D printing in dentistry
Photopolymer 3D printing in dentistry provides numerous benefits, including enhanced customization, greater flexibility, and reduced costs, making this method one of the advantages of 3D printing in dentistry. The following section describes the main advantages of photopolymer 3D printing.
Customization
Customization plays a crucial role in dental care, as every patient has a unique dental anatomy and specific treatment needs. Whether it's dental crowns, bridges, aligners or retainers, the 3D printing process ensures that the appliances fit precisely and comfortably in the patient's mouth. Further, customised surgical guides and templates allow for more precise and minimally invasive procedures, preserving healthy tissues and reducing discomfort.
At the same time, 3D printing streamlines the manufacturing process, for a quicker production of custom dental appliances compared to traditional methods. This reduces the waiting time for patients and leads to streamlined treatment processes as well as ensures patient-centric care
Decentralised manufacturing
While traditional manufacturing processes often involve centralised production facilities, where dental appliances and prosthetics are mass-produced and distributed to various dental clinics, photopolymer 3D printing allows for a more decentralised approach to manufacturing.
Dental clinics can have 3D printers on-site to produce various dental appliances and restorations in-house. This eliminates the need to rely on external suppliers, reduces lead times and enhances the treatment efficiency. In emergency dental cases, 3D printing enables dental professionals to produce temporary restorations and appliances quickly, providing timely relief to patients.
Material efficiency
Material efficiency refers to minimising waste and optimising the use of resources. Photopolymer 3D printing offers several advantages in terms of material efficiency in dentistry. The reason, among others, lies in the layer-by-layer printing method, which adds material only where it is needed.
This UV additive manufacturing process is inherently more material-efficient compared to traditional manufacturing methods, where excess material is removed to create the final object. Further, with this innovative manufacturing method, there's no need to keep a large inventory of pre-made items, which reduces material stockpiling and waste.
Reduced labour costs
As photopolymer 3D printing in dentistry streamlines processes, it simultaneously reduces labour costs for the entire industry. First of all, 3D printing automates the manufacturing process, as the need for manual labour in creating dental appliances and prosthetics can be significantly reduced. Once the 3D printer is set up and the digital design is ready, the printing process requires minimal human intervention.
Having a 3D printer on-site enables dental clinics and laboratories to produce dental appliances and models in-house. This eliminates the need to outsource manufacturing, resulting in cost savings on external production expenses. Therefore, photopolymer 3D printing can lead to significant labour cost reductions and enhanced efficiency for dental practices and laboratories.
Challenges of 3D printing for dental implants
The greatest challenges of 3D printing for dental implants include limitations in material compatibility, as not all materials can be processed by additive manufacturing. Replacement materials may not match the quality of traditional ones, which can pose clinical concerns. Cost is also a significant barrier, as specialised machinery often requires a substantial initial investment.
Further, while AM reduces production time, prefabrication and post-processing can be labour-intensive, which may increase costs. These challenges show that there is still a need for ongoing research and development to optimise material selection, enhance printing capabilities, and address cost-effectiveness in order to fully realise the potential of 3D printing in dentistry.
The usage of photopolymers 3D printing in dentistry
In dentistry, photopolymers are widely used in a specific type of 3D printing technology known as photopolymer 3D printing or stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing. This additive manufacturing technique uses photopolymer resins as the printing material. For more advanced dental applications, integrating techniques like 3D Microfabrication can further enhance the precision and complexity of printed components.
While photopolymers offer numerous benefits in dentistry, it's essential to choose the appropriate resin for each specific application to ensure optimal performance and patient safety.
Dental professionals should consider factors such as biocompatibility, mechanical properties as well as aesthetic characteristics when selecting the proper photopolymer resins for various dental procedures.
Photopolymers are composed of 3 components: monomers, photoinitiators as well as additives. When exposed to specific wavelengths of light, these components undergo a photopolymerization reaction and transform from a liquid or gel-like state into a solid material.
Monomers/Oligomers
Monomers are molecules that have reactive sites enabling them to bond chemically with other monomers. When multiple monomers undergo chemical reactions and join together they form chains known as polymers. This entire process is referred to as polymerization. Monomers are usually organic compounds and the properties and functionalities they possess determine the characteristics of the resulting polymer.
On the other hand oligomers are larger than monomers but smaller than polymers. They consist of monomers and act as intermediate products formed during polymerization. Oligomers serve as a connection between monomers and fully polymerized chains displaying unique properties and functions based on the specific monomer units they contain and how they are bonded together.
Photoinitiators
Photoinitiators are activated by exposure to specific wavelengths of light and initiate the polymerization reaction of monomers and oligomers. When photoinitiators are exposed to light, they absorb the light energy, causing the molecules to transition from a ground state to a higher energy state.
In their excited state, the photoinitiators become unstable and undergo a chemical transformation, leading to the formation of highly reactive species, such as free radicals or cations. These free radicals or cations then initiate the polymerization reaction by attacking and binding to the double bonds present in the monomers or oligomers. As a result, the monomers and oligomers start to form cross-linked polymer chains, transforming the liquid or gel-like material into a solid state.
Additives
Additives are substances added to the photopolymer resin to enhance or modify its properties during the 3D printing process. These additives are carefully selected to optimise the performance of the resin for specific applications, such as dental models, surgical guides, clear aligners and other dental appliances.
Stabilisers are added to the photopolymer resin to prevent premature polymerization or degradation during storage or exposure to light.
Role of Additives in Enhancing Photopolymer Resins for Dental Applications
They help maintain the resin's integrity and ensure consistent printing performance over time.
Modifiers are additives used to adjust specific properties of the photopolymer resin. They can alter the resin's viscosity, curing speed, flexibility or mechanical properties, making it suitable for various 3D printing applications. Some photopolymer resins used in dental 3D printing may also contain colourants. These colourants provide the desired colour to the printed dental appliances, such as clear aligners or surgical guides.
Photopolymers enhance the healthcare landscape
Photopolymer 3D printing advances healthcare, which poses a relief to ageing demographics as well as the overburdened industry as a whole. The process allows the manufacturing of customised instead of one-size-fits-all solutions, while production time and costs decrease significantly.
RAHN is your 3D printing solutions provider and a reliable supply partner of raw materials for 3D printing resins, for the development of high-performance 3D photopolymers. Get in touch and book a call with our experts to find the best solution for your project.
Future potential of 3D printing in dentistry
Once 3D printing in dentistry has reached its full potential, we will be able to see a significant increase in on-demand dentistry, fully customised solutions as well as bioprinting.
On-demand dentistry
The future potential of 3D printing in dentistry lies in the concept of on-demand dentistry, where dental prostheses, and appliances are fabricated quickly and conveniently. New processes such as Volumetric 3D Resin Printing (V3DP) are already paving the way. With advancements in 3D printing technology, dental clinics could potentially offer same-day production of customised crowns, bridges, dentures, and orthodontic appliances, eliminating the need for multiple appointments and lengthy turnaround times.
More customization
While traditional manufacturing already offers custom-made solutions for individual patients, 3D printing in dentistry opens the door for cost-efficient, fast and custom-made solutions – 3 previously contradicting qualities. This enables even patients with a complicated medical history to find cost-efficient solutions that perfectly fit their dental needs.
Bioprinting
This technology is still researched and has the potential to fabricate living tissues and organs using bioinks composed of cells and biocompatible materials. Bioprinting holds the promise for creating custom-made dental tissues, including gums, bones, and even teeth. By harnessing patient-specific cells, researchers envision a future where bioprinted constructs can regenerate damaged or missing dental structures, offering innovative solutions for both tooth replacement and oral reconstruction.
FAQ
Q1: How is 3D Printing Used for Dental Implants?
A1: 3D printing for dental implants allows for the creation of patient-specific implants that are tailored to individual anatomical requirements. This technology is used to manufacture various prosthetic components like abutments and crowns, ensuring a precise fit and improved aesthetics.
Q2: What are the Advantages of Using 3D Printing in Dental Practices?
A2: The advantages of using 3D printing in dentistry include enhanced precision, customization, and material efficiency, leading to better patient care and reduced costs. Additionally, it minimizes waste and optimizes resource use, contributing to more sustainable practices.
Q3: Can 3D Printing be Used for Orthodontic Treatments?
A3: Yes, 3D printing is instrumental in producing custom orthodontic appliances like brackets and clear aligners. It allows for the creation of aligners tailored to each patient's tooth anatomy, improving the fit and effectiveness of orthodontic treatments.
Q4: What Materials are Used in 3D Printing for Dentistry?
A4: Photopolymers are primarily used in dental 3D printing. These materials undergo a chemical reaction when exposed to light, transforming from a liquid to a solid state. The choice of resin is crucial and depends on factors like biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and aesthetics.
Q5: Why is 3D printing for dental implants considered innovative?
A5: 3D printing for dental implants is innovative because it enables the precise and efficient production of patient-specific implants. It reduces production time, enhances customization, and minimizes the risk of surgical errors, making it a game-changer in modern dentistry.
Your personal contact

Christopher Cocklan
3D Printing Business Development Manager EnergyCuring
RAHN USA Corp.
